Introduction:
As the textile sector undergoes constant change, production facilities, warehouses, and other locations must prioritize fire safety as a fundamental duty. Every step of the complex textile production process, from weaving to finishing, presents a risk of fire, which calls for careful consideration and preventative measures. This overview provides a starting point for investigating the various strategies used by the textile industry to improve fire safety regulations. Each component represents a shared commitment to protecting people, protecting property, and maintaining regulatory compliance‚ÄĒfrom the use of flame-resistant fabrics to the installation of cutting-edge detection and suppression systems. Along the way, we will explore the specifics of fire safety procedures in the textile sector and highlight their importance for building a resilient and safe culture in the face of changing circumstances.
Insights of how fire safety procedures are used in the textile industry.
Flame-Resistant materials:
- Textile producers give materials flame resistance using a variety of techniques. This involves treating fabrics with flame-retardant chemicals during the production process or incorporating fibers that are naturally flame-resistant, like meta-aramids (like Nomex).
- Flame-resistant fabrics are crucial to reducing the risk of burns and injuries in high-heat environments in applications like protective clothing for firefighters or industrial workers.
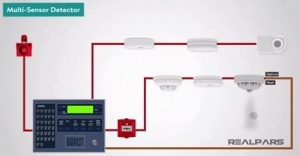
Fire detection systems:
- Textile establishments implement systems that include heat sensors, smoke detectors, and fire alarm panels positioned thoughtfully throughout the building.
- These technologies are linked to detecting heat or smoke early, setting off alarms to notify residents, and starting emergency response procedures.
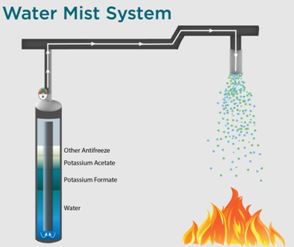
 Fire Suppression Systems:
Fire Suppression Systems:
- In textile factories, automatic fire suppression systems are essential for promptly containing and putting out fires. Sprinklers, water mist systems, and gaseous suppression systems like CO2 are examples of common systems.
- These systems are made to quickly identify and put out fires, reducing the amount of material, infrastructure, and equipment damage.
- To reduce the possibility of fire occurrences, textile manufacturers use these procedures.
- Hazardous items are maintained apart from sources of ignition, storage rooms are kept clutter-free and clean to minimize the chance of a fire spreading, and chemicals finished goods, and flammable materials are all housed in specially designated areas with adequate ventilation and fire-resistant containers.
Emergency Response Planning:
- Textile establishments create detailed emergency response plans that specify how to handle fire situations. These plans outline assembly locations, evacuation routes, and emergency services contact procedures.
- To ensure a prompt and well-coordinated reaction in the case of a fire, personnel participate in regular training sessions and drills that familiarize them with emergency protocols.
Employee Education and Awareness:
- Training sessions are held to inform staff members about fire dangers, safety precautions to take, and how to use firefighting tools including extinguishers and emergency exits.
- Workers receive training on identifying possible fire hazards, reporting safety issues, and efficiently handling emergencies, all of which support the company’s safety culture.
Safety precautions for electrical systems:
- Tight electrical safety regulations are put in place in textile operations to stop electrical fires. To identify and address possible dangers like defective wiring, overloaded circuits, or broken equipment, regular inspections and maintenance of electrical systems are carried out.
- This includes making sure electrical systems and equipment comply with applicable safety standards and codes.
Hot Work Permits:
- When doing heat-generating or spark-producing tasks like welding, cutting, or soldering, there are methods for getting hot work permits.
- To prevent fire accidents during hot work activities, permits specify safety procedures such as the designation of combustible material isolation, the presence of fire watch staff, and fire extinguishers.
 
Maintenance and Housekeeping:
- To reduce the risk of fire, textile facilities keep their workspaces tidy and clean. Maintaining machinery, equipment, and fire protection systems regularly helps to identify and solve potential fire risks, improving overall safety and dependability.
- This includes clearing out combustible debris, managing dust collection, and making sure products are stored properly.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Complying with building codes, fire prevention codes, and occupational safety regulations guarantees that facilities meet minimum safety requirements and protect the health and well-being of employees and surrounding communities.
- Textile manufacturers follow a multitude of local, national, and international fire safety regulations, standards, and codes applicable to their operations.
Conclusion
Fire safety becomes a critical issue in the complex web of the textile sector, permeating both rules and daily operations. Stakeholders in the textile industry exhibit a resolute commitment to reducing fire threats and safeguarding people and property by employing a comprehensive strategy that includes strict regulations, cutting-edge technology, and preventative actions. Every effort demonstrates a shared commitment to promoting a secure and sustainable environment, from the development of flame-resistant materials to the careful supervision of fire detection and suppression systems. Let’s reiterate as we draw to a close our investigation that it is our joint duty to put fire safety first in the textile sector and to embrace cooperation and ongoing development to meet the constantly changing opportunities and difficulties.